Plasma Power
What is plasma used for?
Plasma Power
What is plasma used for?
April 10, 2024
Plasma is an important part of your blood that can be donated. But what is donated plasma used for?
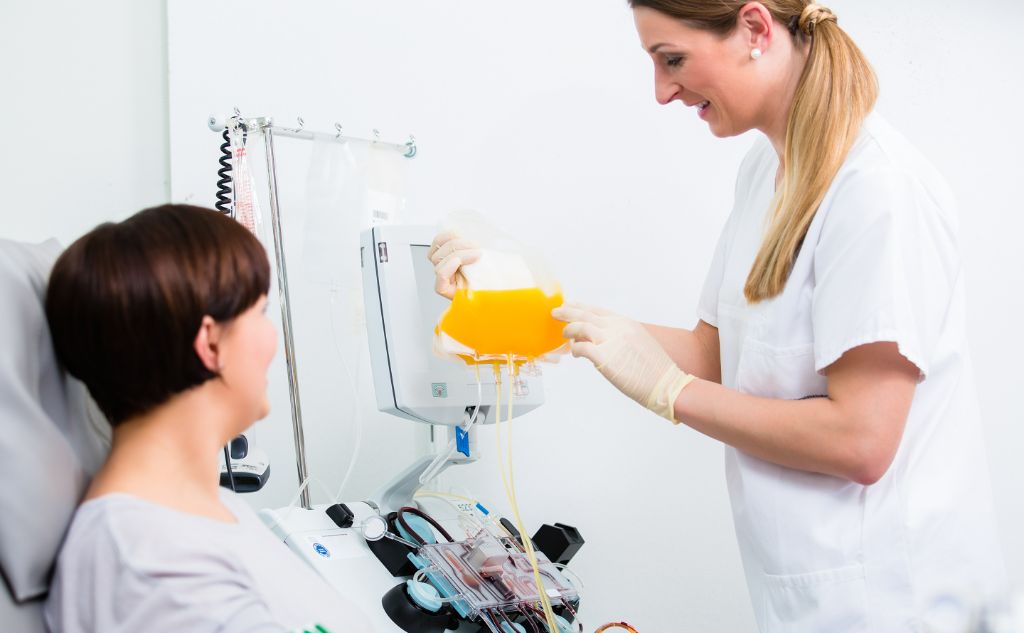
Plasma is the liquid part of your blood. It contains water and a small yet crucial portion of solid substances, such as proteins and antibodies. You can donate plasma along with whole blood or on its own. Plasma donations are vital for shock and trauma treatments, and are also used to make life-saving medicines. Let’s discover the many uses of plasma in medicine.
What is plasma?
Plasma is a part of your blood, specifically the liquid one. In fact, 91-92% of it is water. The remaining percentage of plasma contains vital substances. In particular, these include:
Clotting factors, such as fibrinogen. They give the blood the right consistency and fluidity
Proteins, such as albumin. These have many functions in the body, including transporting oxygen in the blood, contributing to immune function, and enabling digestion
Minerals: They do not provide energy itself but help the organic mechanisms that produce the energy we need
Plasma provides nutrients, enzymes, and hormones to the body and helps remove waste.
Although it is an often-forgotten part of blood, it is the largest one, and its role, when donated, is often life-saving.
What is plasma used for in medicine?
The use of plasma in medicine reached a turning point during World War II when its benefits became clear. It is easier to transport than blood and particularly suitable for shock treatment, such as burns and wounds.
Today, plasma is not only used for emergency treatments but also for chronic, rare, and autoimmune diseases and research.
Your plasma donation can be used for many purposes. Here are some of its most frequent uses:
Accident victims with burns or blood loss from injuries
Excessive bleeding after surgery
People with autoimmune diseases
Amyloid light-chain amyloidosis: a group of rare diseases that cause dysfunctions and organic insufficiencies that can be fatal
Hemophilia: a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of certain blood clotting proteins. A person suffering from a bleeding disorder will have an increased tendency to bleed externally and internally, both spontaneously and after trauma
Myeloma: a type of cancer involving plasma cells
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a rare and genetic blood disorder. It causes a dangerous reduction in the oxygen supply to various organs
Von Willebrand disease: a condition that makes it more difficult for the blood to clot, causing bleeds that last for extended periods of time
Plasma transfusions help with excessive bleeding, and both its proteins and its antibodies can help treat the serious and chronic conditions just mentioned. Typically in these cases, the patient undergoes a treatment called plasmapheresis: the removal, return, or exchange of plasma. This is done with the help of a special machine.
However, the use of plasma for research purposes is equally important, since plasma-derived medicinal products are developed thanks to it.
In conclusion, the plasma you donate is essential for emergencies, but also to help provide the key ingredient for therapies that improve the quality of life of patients suffering from various rare, chronic, autoimmune and genetic diseases.